http://www.ostechnix.com/record-your-terminal-activity-using-script-command


As a System administrator, you might
execute lot of commands in the Terminal everyday. Sometimes you might
want to refer the entire command history along with all respective
outputs later. And, If you’re a programmer and write a program that
displays a really long output in Terminal, you can’t scroll up to
certain limit and can’t view the entire output of your Terminal
session. As a technical writer, I must include what command I entered in
the Terminal and what was the result I got in my articles. So, I
believe It is always a best idea to record the Terminal session, and
keep it aside for future reference. There are many tools out there to
record your Desktop. Unfortunately, there are no such tools for servers
that only has CLI session. Luckily, we have a simple command called script that really helpful to make typescript of everything printed on your Terminal.
Script command allows
you to record everything you do in your Terminal, and saves the output
in a text file. This command comes pre-installed with most Linux, and
Unix-like operating systems.
In this brief tutorial, let me show you how to use script command.
Script command usage
When you’re ready to recording the Terminal activity, just type:
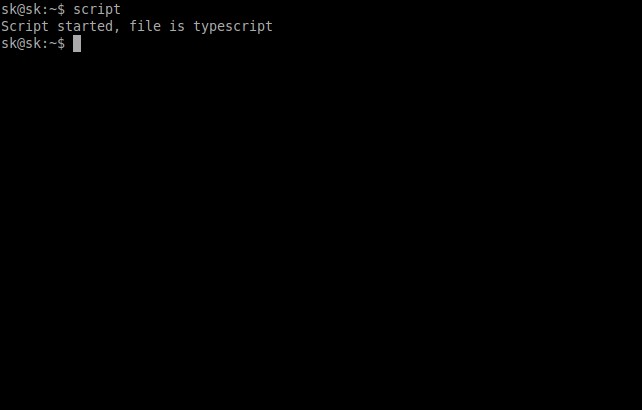
$ script
You will get a message something like below.
Script started, file is typescript

Now, everything you entered in the Terminal will be saved in a file called typescript.
Also, you can give a custom name to the typescript by specifying a file name of your choice as shown below.
$ script -a my_terminal_session
Now, Let us type few commands, and see how it works.
$ whoami
$ uname -a
$ cd /home/sk/Soft_Backup
$ ls -l
$ mkdir ostechnix
$ rmdir ostechnix
That’s enough for now. You can try as
many commands as you want to record. Once you are done, type ‘exit’ in
the Terminal to stop recording.
$ exit
Sample output:
exit Script done, file is typescript
As you see in the above screenshot, the
script command will be stored in file called “typescript” in the current
working directory.
Now, let us go ahead, and check what we did so far in the Terminal.
Check script command output
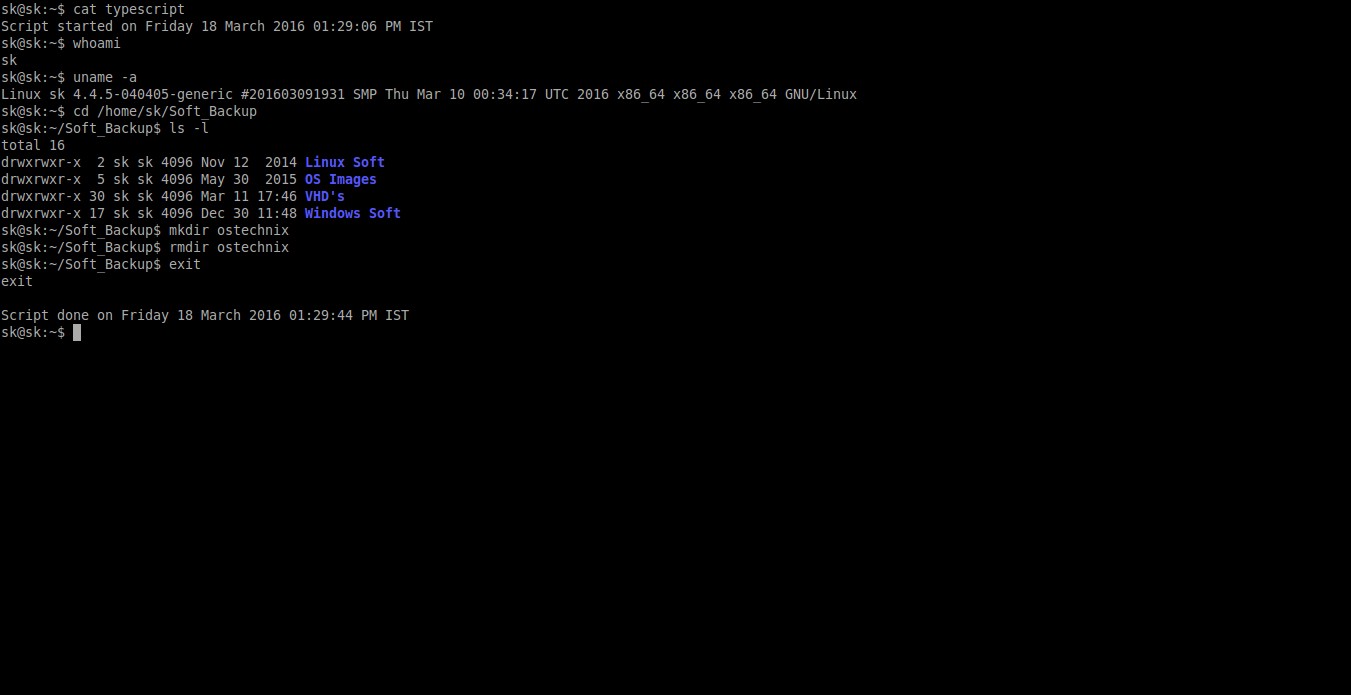
$ cat typescript
Sample output:
Script started on Friday 18 March 2016 01:29:06 PM IST sk@sk:~$ whoami sk sk@sk:~$ uname -a Linux sk 4.4.5-040405-generic #201603091931 SMP Thu Mar 10 00:34:17 UTC 2016 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux sk@sk:~$ cd /home/sk/Soft_Backup sk@sk:~/Soft_Backup$ ls -l total 16 drwxrwxr-x 2 sk sk 4096 Nov 12 2014 Linux Soft drwxrwxr-x 5 sk sk 4096 May 30 2015 OS Images drwxrwxr-x 30 sk sk 4096 Mar 11 17:46 VHD's drwxrwxr-x 17 sk sk 4096 Dec 30 11:48 Windows Soft sk@sk:~/Soft_Backup$ mkdir ostechnix sk@sk:~/Soft_Backup$ rmdir ostechnix sk@sk:~/Soft_Backup$ exit exit Script done on Friday 18 March 2016 01:29:44 PM IST

Voila! As you see in the above output,
Script command recorded and displayed everything I have entered in the
Terminal. For your easy understanding, I have marked the commands that I
executed in bold letters.
You could use the output for your assignment, or just save this output for future reference, and so on.
For further details, I recommend you to refer the man pages.
$ man script
That’s all I can write about script
command now. If you want a hardcopy record of the Terminal session for
future reference, or for a assignment, script command is good tool to
try.
If you find this tutorial, please share it on your social networks and support OSTechNix.
Cheers!

No comments:
Post a Comment